My Alzheimer's Journey
Part 6 - The Connection Between Neurogenesis and Alzheimer's
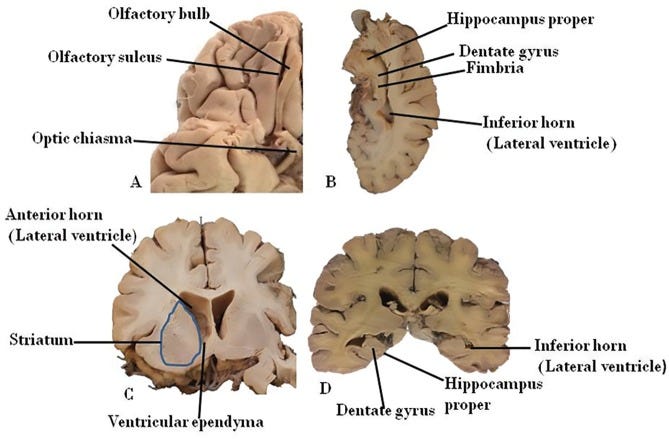
Neurogenesis is the process by which new neurons are formed in the brain. This process is most active while a baby is developing in the womb and is responsible for the production of the brain’s neurons. The development of new neurons continues during adulthood in two regions of the brain. Neurogenesis takes place in the subventricular zone (SVZ) that forms the lining of the lateral ventricles and the subgranular zone that forms part of the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus area.
The concept of neurogenesis in adults has historically been a controversial topic among researchers. While some researchers report that a sharp drop in neurogenesis occurs as the human brain ages, other researchers report that neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus of human brains persists into old age. For the most part, adult neurogenesis is now generally acknowledged.
Several studies suggest that neurogenesis in adults plays a role in memory and learning systems. Altered neurogenesis has been identified in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), in both human AD brains and AD rodent models.
Is impaired neurogenesis associated with cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s? There needs to be much more research to answer that question definitively.
It is known that AD patients show decreased levels of adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN) compared to healthy individuals. The decline in neurogenesis may begin in the early stages of cognitive decline, such as mild cognitive impairment (MCI), before the full development of AD symptoms.
Based on the research I have recently studied, I believe neurogenesis has numerous anti-aging and cognitive benefits. Mood regulation, reduced depression, reliance to stress, improved memory, and developing new learning strategies are some of the benefits.
The good news is that you can control adult neurogenesis.
According to a recent article published by the Regeneration Center of Thailand, there are four ways to naturally increase neurogenesis:
Intermittent fasting between meals along with a calorie restriction diet (20-30% less than average intake).
Regular intake of flavonoid compounds that are found in blueberries and dark chocolate. Yum!
Regular eating of Omega-3 fatty acids that are found in fatty fish such as salmon.
Aerobic and cardiovascular exercise
Other studies indicate that stimulating and challenging your brain will increase neurogenesis.
What are your thoughts? Do you take steps to stimulate neurogenesis?